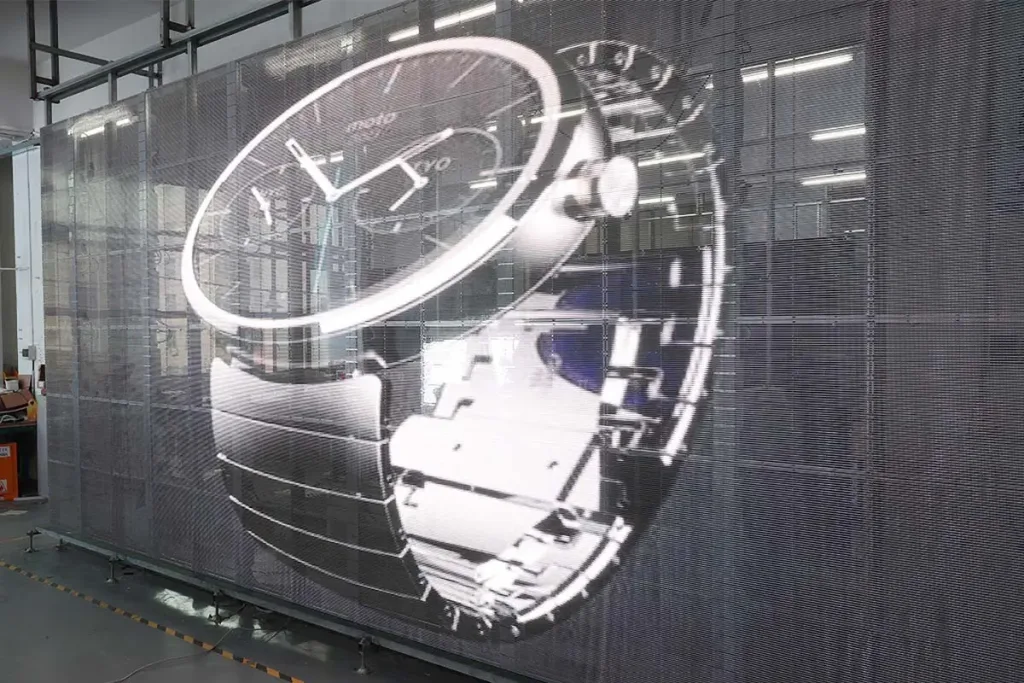
MIP technology (Micro LED in Package) is revolutionizing the LED display industry—it tackles the biggest hurdles in Micro LED mass production: complex assembly, frequent dead pixels, and sky-high costs.
Dubbed the “ultimate display tech of the future”, Micro LED promises unbeatable brightness, insane contrast, crazy-long lifespan, and energy efficiency. But there’s a catch: these tiny LEDs are a nightmare to manufacture. It is said that the emergence of MIP technology will change this dilemma. Is this really the case?
catalogue
- 1. MIP texnologiyası nədir?
- 2. MIP texnologiyasının üstünlükləri hansılardır?
- 3. MIP LED texnologiyasının çatışmazlıqları hansılardır?
- 4. MIP LED ekranın tətbiqləri hansılardır?
- 5. MIP LED və Digər LED Texnologiyaları
- 6.Trend: MIP-in gələcəkdə istifadəsi nədir?
- 7. MIP Texnologiyası haqqında tez-tez verilən suallar
- 8. Nəticə
1.What is MIP technology?
MIP technology, short for Micro LED in Package (MIP LED), is a packaging technology for LED displays. It involves packaging numerous tiny Micro LED chips within individual “boxes” before assembling them onto a display panel.
In a nutshell, it’s “packaging first, assembly later.”
1.1 What is an MIP LED Display?
An MIP LED display is a type of LED screen built using MIP (Micro LED in Package) technology.
Key Features:
- Crystal-Clear Resolution – Uses ultra-tiny LED chips, with pixel pitches as small as 0.4mm and densities over 200 PPI, eliminating the grainy look of traditional LED screens for lifelike visuals.
- Energy Efficient – Thanks to high-efficiency micro LEDs, these displays deliver bright images while keeping power consumption low.
- Strong Anti-Interference – The modular design shields each LED chip inside a protective casing, reducing electromagnetic interference.
On top of that, MIP LED display offers high brightness, deep contrast, and wide color gamut, making them the top choice for premium commercial displays.
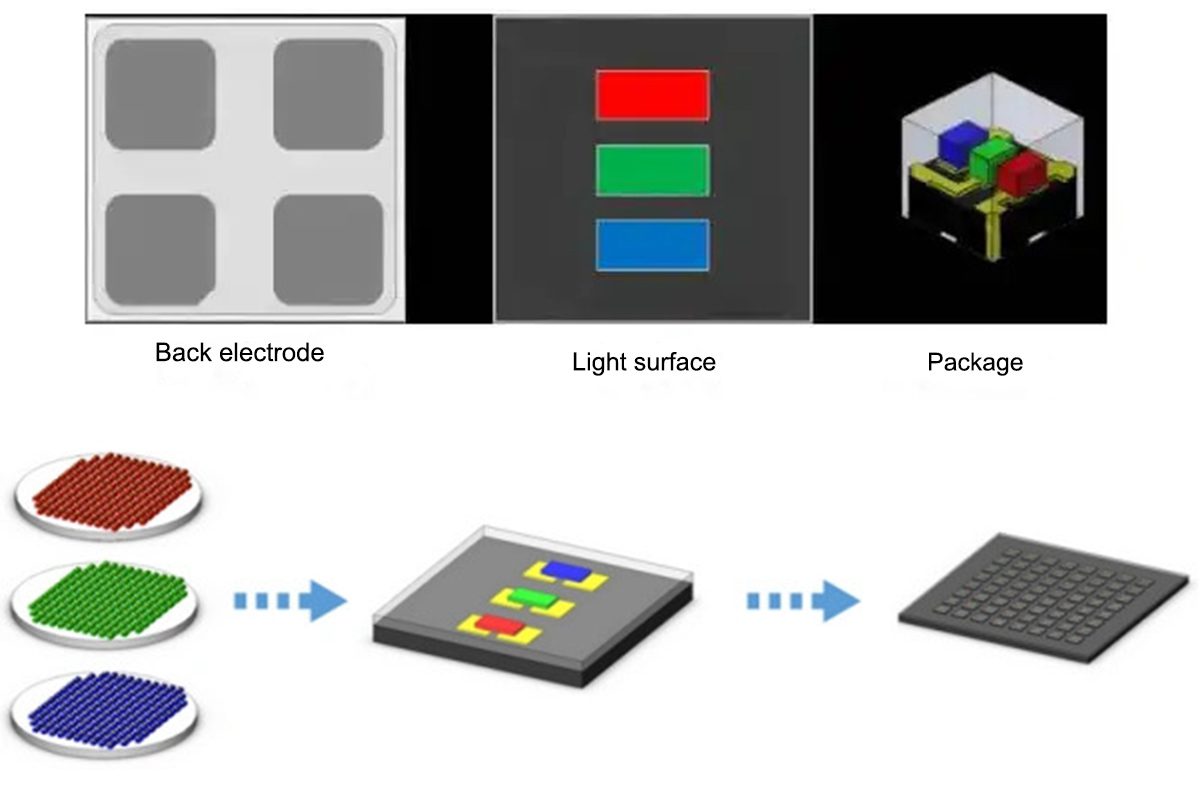
MIP technology process (simplified version):
- Micro LED chips transferred to substrate to form an array
- Distributed packaging
- Cutting and sorting
- Packaging onto the carrier board
- Cutting the carrier board
- Optical and electrical performance testing
- Transferred to PCB or glass substrate
- Final optical and electrical testing and calibration
- Large-scale packaging into complete LED displays
1.2 How Does MIP Technology Work?
Think of it like this: Instead of moving sand grain by grain (which is slow and tedious), why not pack it into standard bags first? That way, you can transport and stack them way faster.
In this analogy:
Sand grains = Micro LED chips (each just 30–100 microns wide—thinner than a human hair!).
Sandbags = Pre-assembled “packages” containing dozens or even hundreds of micro LEDs.
MIP technology groups these tiny LEDs into larger, easier-to-handle “packages” before installation. So instead of placing millions of microscopic chips one by one, manufacturers just work with these pre-packaged units, making production much simpler and more efficient.
2. What are the advantages of MIP technology?
MIP technology has become a key driver for the commercialization of Micro LED due to its ability to solve three major challenges in traditional manufacturing: low production efficiency, low yield, and high overall costs.
2.1 10x Improvement in Production Efficiency
Before: Each Micro LED chip, measuring only 30-100 microns, had to be transferred individually with extreme precision (±1.5 microns). This process was like stitching with a microscope—slow (only 3-5 chips per second) and prone to errors.
Now: MIP technology pre-packages dozens or even hundreds of chips into standardized 5mm modules, allowing for placement errors of up to ±50 microns. This modular installation significantly reduces the complexity of producing Micro LEDs and speeds up the process.
2.2 Breakthrough improvement in yield rate
Before: Due to the tiny size of Micro LED chips, the transfer process was very error-prone, and the allowable error margin was only 1.5 microns. If even one chip was defective, it would cause bright spots or malfunctioning areas on the screen, and attempts to fix it would often make things worse.
Now: With MIP technology, multiple Micro LED chips are integrated into larger modules, making production easier and reducing the likelihood of errors. The chips are screened during the packaging phase (wafer-level testing), greatly decreasing the chances of defective spots.
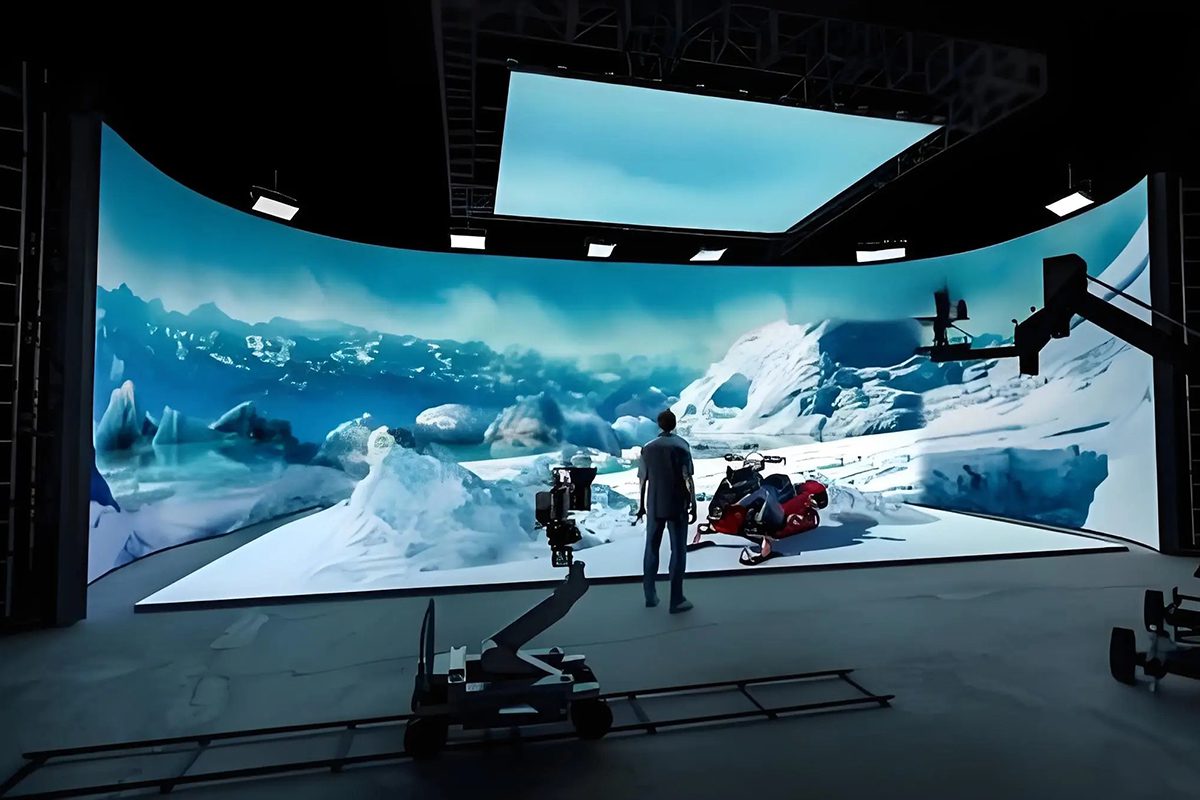

2.3 Significant Reduction in Production Costs
Before: Producing Micro LEDs required specialized equipment worth tens of millions of dollars, with labor costs around $100 per square meter and material wastage as high as 15%. These factors pushed up the final product prices.
Now: MIP technology streamlines the manufacturing process and reduces reliance on specialized equipment. The packaging process can be done on a larger scale and with higher efficiency, leading to increased output and lower costs.
2.4 Beyond these benefits, MIP technology also brings more advantages, including:
- The use of surface-mount technology, which enables companies without massive transfer capabilities to produce high-quality, ultra-fine pitch MIP LED screens.
- Achieving pixel pitches as small as P0.7 or even smaller for incredibly detailed image quality.
- Strong shock and vibration resistance, making the screens very durable.
3. What are the disadvantages of MIP LED technology?
High Cost
The production cost of MIP technology is still quite high, making it 3-5 times more expensive than regular LED screens. This is mainly due to the need for high-precision packaging techniques and advanced manufacturing equipment.
Technology is Still Evolving, No Industry Standard
MIP and COB technologies are somewhat in competition, but MIP is far from as mature or widely adopted as COB. There is also no complete industry chain or supply chain yet, and technical collaboration within the industry remains a significant challenge.
No Localized Repair for Dead Pixels
If dead pixels occur, the entire screen needs to be replaced. While repairs have become easier, the cost has also risen sharply. Unlike SMD screens, where individual LEDs can be replaced, MIP screens don’t allow for such specific repairs.
Poor Heat Dissipation
Traditional LED screens often use heat sinks or heat-dissipating back panels to cool the chips, but with MIP technology, multiple chips are packaged into a single unit. This design can hinder the effective release of heat, leading to poorer heat dissipation.
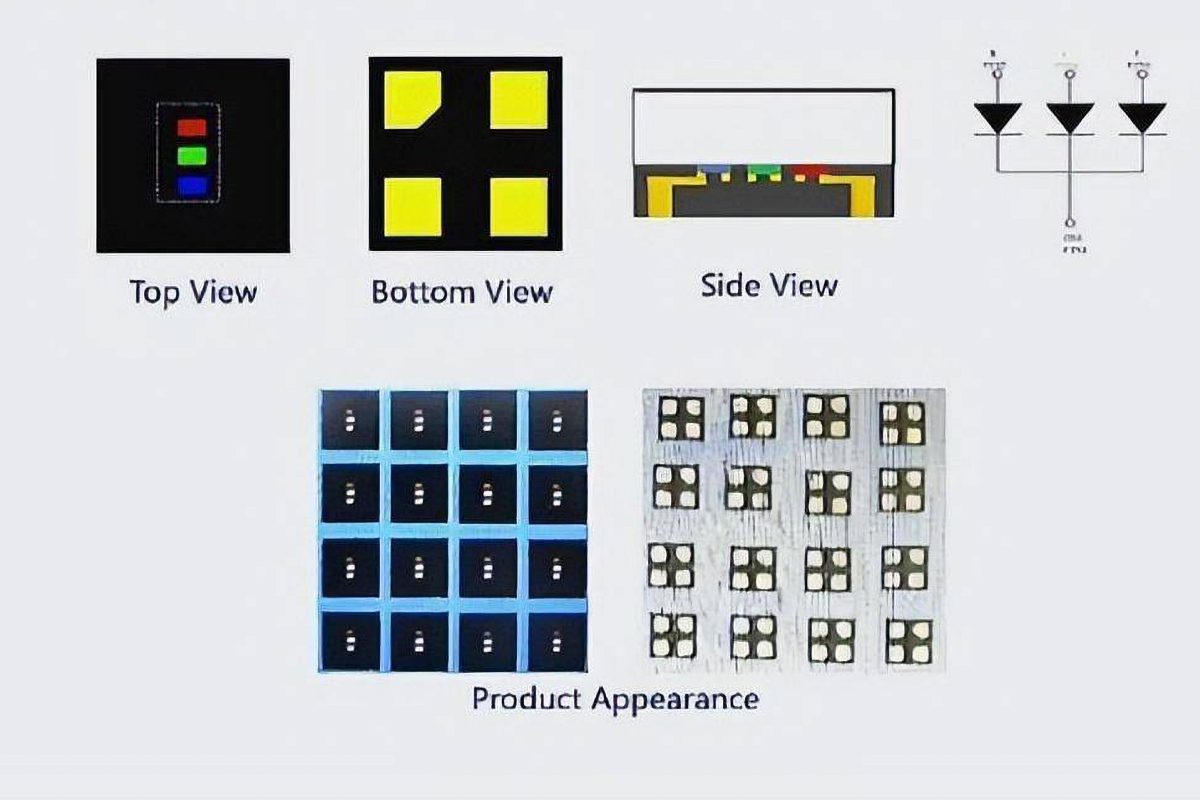
4.what are the applications of MIP LED screen?
Currently, MIP LED screens are not widely used and are mostly limited to high-end display applications.
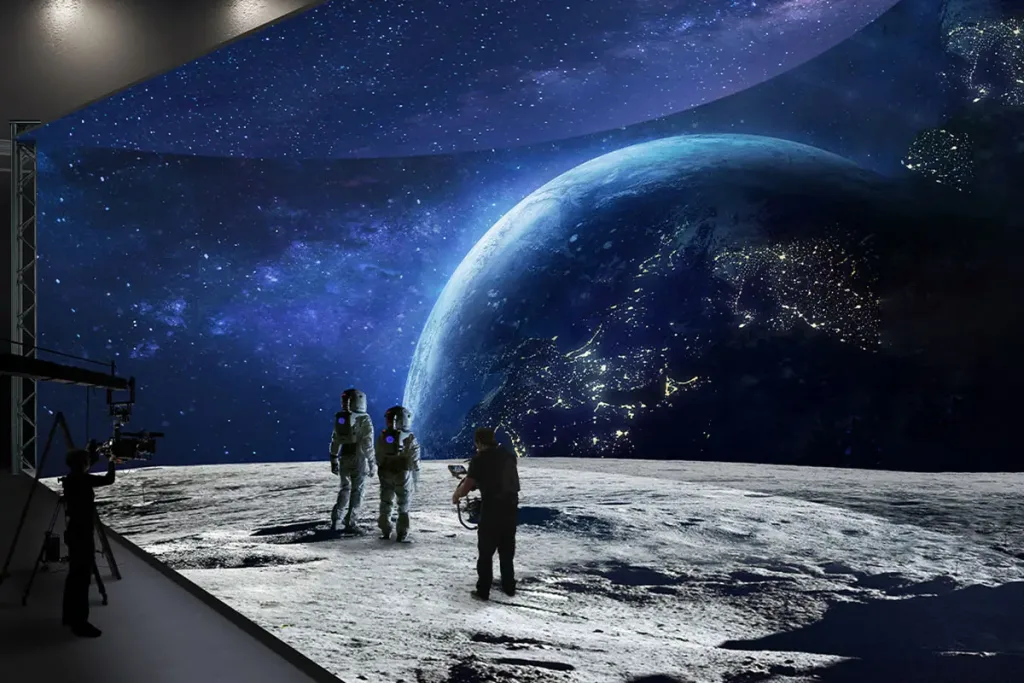
Virtual Production LED Wall: Virtual shooting technology relies on precise display equipment to create realistic digital environments. MIP LED screen, with its high resolution, vibrant colors, and stable display, are perfect for virtual filming in the film and advertising industries.
Home Theater: Although MIP technology hasn’t yet spread to the consumer market, it has started making its way into high-end home theaters. With 8K resolution, 10,000 nits peak brightness, and a pixel pitch of 0.4mm, an MIP LED cinema screen offers a flawless viewing experience, even from just 2 meters away, with no visible pixelation.
High-End Art Exhibitions: MIP screens’ high color accuracy and stability make them ideal for accurately reproducing artwork. Some cutting-edge art exhibitions have begun using this technology to provide immersive displays while protecting the original works.
High-End Conference Rooms: MIP LED screens not only deliver high resolution and accurate color reproduction but also support multi-touch functionality, making meetings and presentations more efficient and interactive. This makes them perfect for high-demand environments like multinational corporations and research centers.
Command Centers: MIP screens’ reliability and durability are particularly beneficial for environments that require continuous 24/7 operation, such as emergency command centers or traffic management hubs.
5. MIP LED vs Other LED Technologies
5.1 What other packaging technologies are used for LED displays?
COB Packaging
Advantages:
- Supports ultra-fine pixel pitches, such as P0.9 and P0.7.
- Resolution can reach 8K or even 16K.
- Provides uniform colors, shock-resistant, moisture-proof, and dust-resistant, making it less likely to lose LEDs.
Disadvantages:
- Requires high-end equipment and is more expensive.
- If it breaks, the entire module needs to be replaced.
SMD Packaging
Advantages:
- Mature technology, easy to mass-produce, and more affordable.
- Individual LEDs can be replaced, making repairs more cost-effective.
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to achieve pixel pitches smaller than P1.5.
- LEDs are exposed, which makes them prone to dust and water damage, affecting display quality over time.
5.2 what is the difference between MIP and COB LED?
| MIP LED Technology | COB LED Technology | SMD LED Technology | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Package structure | Integrate multiple Micro LED chips into a package and then assemble them into a display panel | The bare chip is directly fixed on the substrate. After packaging, there is no traditional packaging shell. It is connected by fluorescent glue and gold wire. | A single LED chip is first packaged into an independent lamp bead and then soldered and mounted on the PCB |
| Integration density | The integration density per unit area is extremely high, which can achieve ultra-small pixel pitch (below P0.1) | Chip density is 50-200 chips/cm², and the pitch can be compressed to 0.1mm (Mini LED field). Common pitches are P0.6~P1.0 | The spacing is usually >0.5mm (mainstream 0.8-1.2mm), and the integration is low |
| Performance Comparison | High brightness, high contrast, average heat dissipation | High brightness, high contrast, and optimal heat dissipation | Average brightness and contrast, poor heat dissipation |
| production costs | Above average | High | Low |
| Application Market//Scenario | Mainly in the market below P0.4, virtual photography, smart watches and other wearable consumer electronics | Cinema-level giant screens, conference room integrated screens and other small-pitch screens | Mature industrial chain and low equipment investment |
6.Trend: what is the use of MIP in the future?
From High-End Displays to the Mass Consumer Market
As manufacturing processes continue to improve, the production efficiency of MIP LED displays will increase significantly, and production costs will drop. This will allow MIP LED displays to gradually move from the high-end market into the mass consumer market. For example, we could see MIP technology becoming more common in home theaters, office displays, and personal devices in the future.
From Single Industry Applications to Multiple Industries
MIP LED displays will expand into various industries, including retail, education, transportation, and public information systems. In retail, MIP displays can be used for digital signage to showcase ads and product information. In education, they can serve as interactive teaching tools.
Integration with Other Smart Technologies
MIP displays will evolve from being just static display devices to integrating with AI technology, enabling smart displays and enhanced control features.
7. FAQs about MIP Technology
8. Conclusion
Overall, MIP technology is a very promising innovation, but whether or not to choose MIP screens depends on balancing your needs with your budget. If you have more questions or want to learn more about MIP technology, feel free to reach out—I’d be happy to help!