When buying a monitor or custom LED display, the screen contrast ratio is a key spec you’ll often hear about. But many people don’t really understand it—leading to problems like:Paying top dollar for a screen that doesn’t deliver true contrast,Professional mistakes in critical settings (e.g., medical diagnosis or video editing) due to poor display quality,Outdoor ads becoming unreadable in bright light, wasting your investment.
So, what exactly is screen contrast ratio? How is it measured? Does a higher number indicate better performance? Understanding this will help you avoid overpaying for unnecessary specs and pick the ideal contrast ratio for your needs.
catalogue
1.what is contrast ratio?
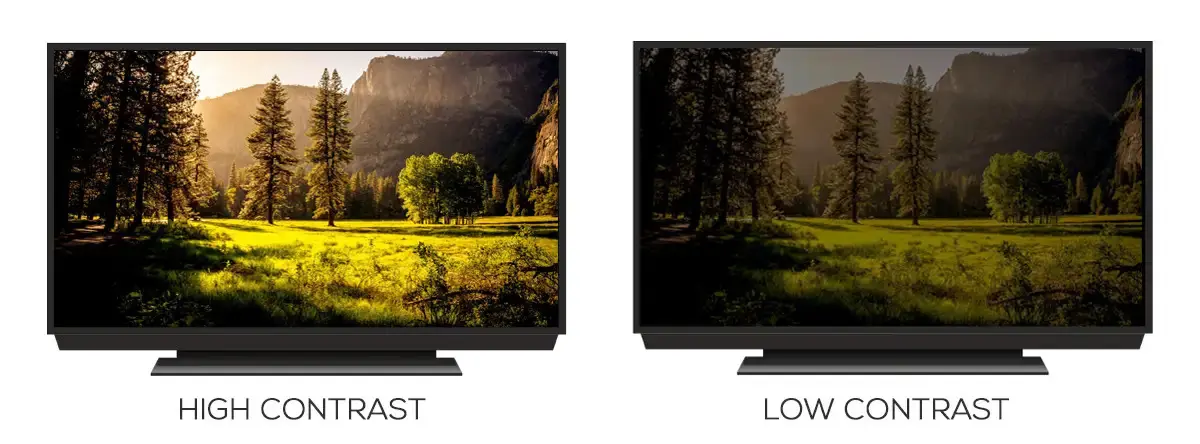
Simply put, the monitor contrast ratio is the difference in brightness between the brightest white and the darkest black on the screen. A higher display contrast means deeper blacks and brighter whites, which makes the image appear more vibrant and full of depth.
Without a good screen contrast ratio, the picture may look dull, and details can be unclear. In other words, it’s a key factor in seeing clear, rich images on your screen.
1.1 Types of Screen Contrast Ratio
Static Contrast Ratio: This measures the brightness ratio between the brightest white and the darkest black on a screen, usually under a stable, static image.
For example, if the brightest white is 300 cd/m² and the darkest black is 0.1 cd/m², the static contrast ratio would be 300:0.1 = 3000:1.

Dynamic Contrast Ratio: This measures the contrast created by the changes in brightness when the screen switches scenes. Dynamic contrast numbers are often much higher, even reaching millions to one. However, they reflect extreme or instant changes in brightness and may not accurately represent real-life performance.
ANSI Contrast Ratio: This is measured by displaying specific grayscale test patterns (like alternating black and white squares) and reflects the contrast found in everyday images, making it a more accurate representation of actual screen performance.
Why is Screen Contrast Ratio Important?
- Higher contrast = deeper blacks + purer whites → More vibrant, clearer images.
- Low contrast = grayish blacks, yellowish whites → Overall blurry, lack of depth.
1.2 What does Screen Contrast Ratio do?
The screen contrast ratio helps improve the display by balancing the light and dark areas, making the image clearer and more vibrant, just like how our eyes naturally perceive things.
Image Details: A higher contrast ratio enhances detail visibility, particularly in low-light or high-brightness conditions. For example, in dark scenes in movies or games, high contrast helps show more shadow details, like a person’s face or subtle changes in the background, instead of just pure black.
Image Depth: With an enhanced contrast ratio, displays render a more dramatic divide between illuminated and dimmed areas. As a result, the picture gains greater spatial depth and visual hierarchy.
For example, when a person stands against a bright background, the contrast between the light background and the shadows on the person makes them stand out more. Things like mountain outlines, facial expressions, and lighting effects in night scenes all look sharper and more realistic with a higher screen contrast ratio.
Color Performance: High contrast makes colors appear more vivid and bright, especially in detailed images and videos. It helps prevent colors from looking dull or washed out due to a low contrast ratio.
Viewing Experience: With better display contrast, the screen delivers clearer and sharper images, reducing eye strain caused by poor detail or overexposure. This makes activities like work, watching videos, and design more comfortable, while also enhancing gaming and entertainment experiences.
1.3 Factors That Influence Screen Contrast Ratio
The contrast of a monitor or LED display is an inherent feature of the device, but it can vary depending on several factors. The main factors include:
Display Panel Type: Different display technologies (like LCD, LED, OLED, etc.) have different contrast performances. Generally, OLED monitors have higher contrast as each pixel can be independently powered off, enabling absolute black reproduction.
Screen Brightness: The higher the screen’s brightness, the better its contrast usually is. Monitors with lower brightness may struggle to display deep blacks, leading to a lower contrast ratio.
Ambient Light: The light in your environment can also affect how you perceive the monitor contrast ratio. In bright environments, even if the contrast is high, the surrounding light can make the image look unclear. On the other hand, in dim lighting, higher contrast will stand out more.
Display Content: Different images or video content can impact how the contrast performs. For example, brighter images may make the contrast stand out more, while pure black or pure white content doesn’t show as much contrast difference.
1.4 What is a low or high contrast screen?
It’s easy to tell the difference between a low and high contrast screen, even with just your eyes.
Low Contrast Characteristics:
- Blacks look like dark gray.
- Whites aren’t pure white, they may appear slightly yellow.
- The overall image seems a bit blurry, like it’s covered by a thin fog.
- This effect is especially noticeable in low light environments (such as watching movies at night).
High Contrast Characteristics:
- Blacks appear close to pure black (OLED can even reach ∞:1).
- Whites are bright and pure.
- The image looks clear and three-dimensional.
- The screen remains clear even in bright light (like outdoor advertising screens).
If we use specific numbers to measure display contrast:
- Low: 500:1 ~ 1500:1.
- High: 3000:1 ~ ∞:1 (OLED can reach theoretical infinity).
2.What is the difference in OLED/LED/LCD screen contrast ratio?
Different display technologies (OLED, LED, LCD) have significant differences in screen contrast ratio, and these differences come from how each type works and displays images.
2.1 OLED Screen Contrast Ratio
OLED screens offer the highest contrast among all screen types, with virtually no upper limit for contrast. Each pixel can light up individually or turn off completely, allowing for true “black.”
In practice, OLED screens can make black areas appear completely dark, while bright areas can remain at very high brightness levels, creating incredible contrast between light and dark. For example, when watching the famous black hole scene in Interstellar, an OLED screen can perfectly show the deep space background and the bright stars, with a clear distinction between the stars and the black hole.

Technical Analysis:
- Each OLED pixel is an independent light source, so no backlight is required.
- The on/off state of each pixel can be controlled precisely.
- The switching speed is extremely fast (in microseconds), preventing motion blur.
- Theoretically, the black brightness is 0 nits, resulting in a contrast ratio of ∞:1.
Practical Effects:
- When displaying HDR content, bright areas can reach over 1000 nits, while dark areas remain perfectly black, making it the top choice for high-end displays.
- In medical imaging, OLED screens can clearly distinguish the smallest grayscale changes in X-rays.
- In gaming, both dark details and bright effects are perfectly displayed.
- During professional color grading, OLED screens can accurately reproduce the most subtle light-to-dark transitions.
2.2 LED Screen Contrast Ratio
The contrast of LED displays mainly depends on the design of their backlighting system. Unlike traditional LCDs, LED screens use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the backlight source and enhance contrast through local dimming technology. Currently, mainstream LED displays typically have contrast ratios ranging from 1000:1 to 5000:1.
Technical Analysis:
- The contrast of an LED screen mainly depends on its “lighting method.”
Edge-lit: LED strips are placed around the edges of the screen, and light is evenly spread through a light guide plate. However, blacks may not be deep enough, similar to reading a newspaper on a cloudy day.
Direct-lit: LED chips are directly arranged behind the screen, allowing for local brightness control. This results in purer blacks, like a room with the lights off.
- High-end products are equipped with local dimming features (like Mini-LED).
- Regular LED displays offer around 1000:1 contrast, while high-end Mini-LED displays can achieve contrast ratios of over 10,000:1.
Choose according to usage:
| Usage scenarios | Recommended Type | Expected Results |
|---|---|---|
| Home Theater | Thousand-zone Mini-LED | Close to OLED |
| E-sports games | High refresh rate direct-lit LED | Clear light and dark |
| Supermarket advertising screen | Ordinary direct-lit LED | Sufficient and cheap |
However, it should be noted that the black performance of LED screens still cannot reach the level of OLED, and slight backlight leakage may be observed when watching in a completely dark environment. However, it may be a screen that is closest to the level of OLED, and the price will be much lower than OLED, making it a very cost-effective choice.
2.3 LCD Monitor Contrast Ratio
In terms of screen contrast ratio, LCD and LED displays have many similarities, but there are some key differences. An LED display is essentially based on LCD panel technology, with LEDs used as the backlight source.
Technical Analysis:
- LCD displays’s light is evenly distributed, but black areas often suffer from light leakage.
- Liquid crystal molecules control the passage of light, improving the display of bright areas, but the performance of black areas tends to be weaker.
- Some high-end LCDs use local dimming technology to adjust the brightness in specific areas, which can improve the screen contrast ratio.
Practical Effects:
For everyday office work, web browsing, or watching standard videos, the LCD monitor contrast is usually sufficient.
In design and photography work, some high-end LCD monitors perform quite well. However, compared to LED or OLED displays, their black levels may fall short.
3.Which Screen Contrast Ratio Wins for YOUR Needs?
Indeed, a higher monitor contrast ratio can deliver more stunning display effects – deep blacks, bright whites, and richer detail levels. But just like buying a sports car, where more horsepower isn’t always better, choosing a display’s contrast ratio also requires balancing performance with your budget.
3.1 Daily life and entertainment requirements for monitor contrast ratio
| Usage Scenario | Recommended Contrast Ratio | Suitable Technology | Why This Choice? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Office Work | 1000:1~1500:1 | IPS LCD Screen | Clear text without eye strain, lowest cost |
| Home Theater | 3000:1~5000:1 | VA Panel/Mini-LED | Rich dark scene details, excellent HDR performance |
| Professional Design | 5000:1+ | OLED/High-end Mini-LED | Accurate color and brightness reproduction |
| Competitive Gaming | 3000:1~10000:1 | High Refresh Rate LED Screen | Fast response + clear visibility of enemies in dark areas |
3.2 Commercial/advertising requirements for screen contrast ratio
In large-scale events such as commercial exhibitions and stage performances, LED screens have become the preferred solution for large-scale visual presentations due to their advantages of seamless splicing and flexible size.
|
Usage Scenario |
Recommended Contrast Ratio |
Suitable Technology |
Why This Choice? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storefront Display | 5000:1+ | Small-pitch LED Screen | Remains clearly visible in high-brightness environments without being overly expensive |
| Outdoor Advertising Billboards | 8000:1+ | Outdoor LED Screen | High contrast ensures visibility even in direct sunlight or strong UV conditions, preventing a washed-out or gray appearance |
| Stage Performance Backdrop | 10000:1+ | Ultra HD Rental LED Screen | Enhances image depth, precisely displays highlights and shadows, creating a more dramatic stage effect |
| Virtual Production Studio | 10000:1+ | Cinema-grade Mini-LED Screen | Ideal for high dynamic range (HDR) and precise lighting effects, delivering rich details and color gradation to enhance integration between virtual backgrounds and actors |
|
High-end Meeting Room |
4500:1+ | Ultra-slim All-in-One LED Meeting Screen | Offers detailed performance, suitable for prolonged surveillance and real-time data display. |
| Security Monitoring Center | 5000:1+ | Seamless LED Video Wall | Offers detailed performance, suitable for prolonged surveillance and real-time data display. |
4. Can You Adjust Screen Contrast Ratio?
While monitor contrast ratio is a fixed parameter set at the factory (just like the megapixels of a smartphone camera – it’s what you get when you buy it), don’t worry! There are still ways to make the image look clearer and more vibrant.
4.1 How Can Regular Users Adjust Screen Contrast Ratio?
For everyday users, while you can’t change the hardware contrast of the screen itself, there are a few simple ways to make the picture look sharper and more layered:
Use the Monitor’s Menu Settings: Many monitors come with a contrast adjustment option (usually found in “Image Settings” or “Display Mode”). Increasing the contrast can make blacks and whites more distinct. But be careful:
- If the contrast is too high, whites may become overexposed, and details may be lost.
- If the contrast is too low, the image will appear dull and grayish.
Use Software Optimization: Many LED displays come with dedicated control software (like NovaLCT, Linsn, Colorlight, etc.). These programs allow you to adjust brightness, contrast, color temperature, and other display settings.
Adjust the Content: If the photo or video you’re displaying has low contrast, even a high-contrast monitor won’t make the image clearer. You can use photo editing software or video editors to boost the contrast of the image or video. Also, make sure to enable the monitor’s HDR mode when playing HDR content.
4.2 How Can Professionals Improve Screen Contrast Ratio?
For display manufacturers and technicians, improving the contrast ratio requires a hardware-level approach. For example, in the case of LED displays, the following methods can be used:
Core Material Upgrades:
- Black LED Chips: Using special coated LEDs from manufacturers like Nichia reduces lateral light diffusion, resulting in a 40% improvement in contrast.
- Dark Substrate: Replacing the traditional white PCB with matte black substrates reduces reflections between pixels.
- Optical Coating: Adding anti-reflective nano-coatings improves contrast retention in outdoor environments by 60%.
Packaging Technology Innovations:
- COB (Chip-on-Board) Technology: Directly packaging chips eliminates pixel gaps, increasing the effective light-emitting area to 98%.
- Flip-Chip Technology: Reduces reflection from the solder pads and, when combined with dark silicone packaging, lowers black field brightness to 0.01 nits.
5. Three Accurate Ways to Test Contrast Ratio
5.1 Methods for Testing Screen Contrast Ratio
Method 1: Using Professional Calibration Tools
The most accurate way to test the screen contrast ratio is by using professional calibration tools like a colorimeter or spectrophotometer. These tools can measure the brightness of the brightest white and the darkest black on the display, then calculate the contrast ratio.
Required Tools:
- 16-step checkerboard black-and-white alternating pattern (available online).
- Light meter, such as X-Rite i1Display Pro or Datacolor SpyderX.
- A dark room with ambient light < 5 lux.
Steps:
- Display a full white screen and measure the brightness at the center (L_white).
- Display a full black screen and measure the brightness at the same position (L_black).
- Contrast Ratio = L_white / L_black.
This method is internationally recognized in labs, providing very reliable results and is easy to perform.
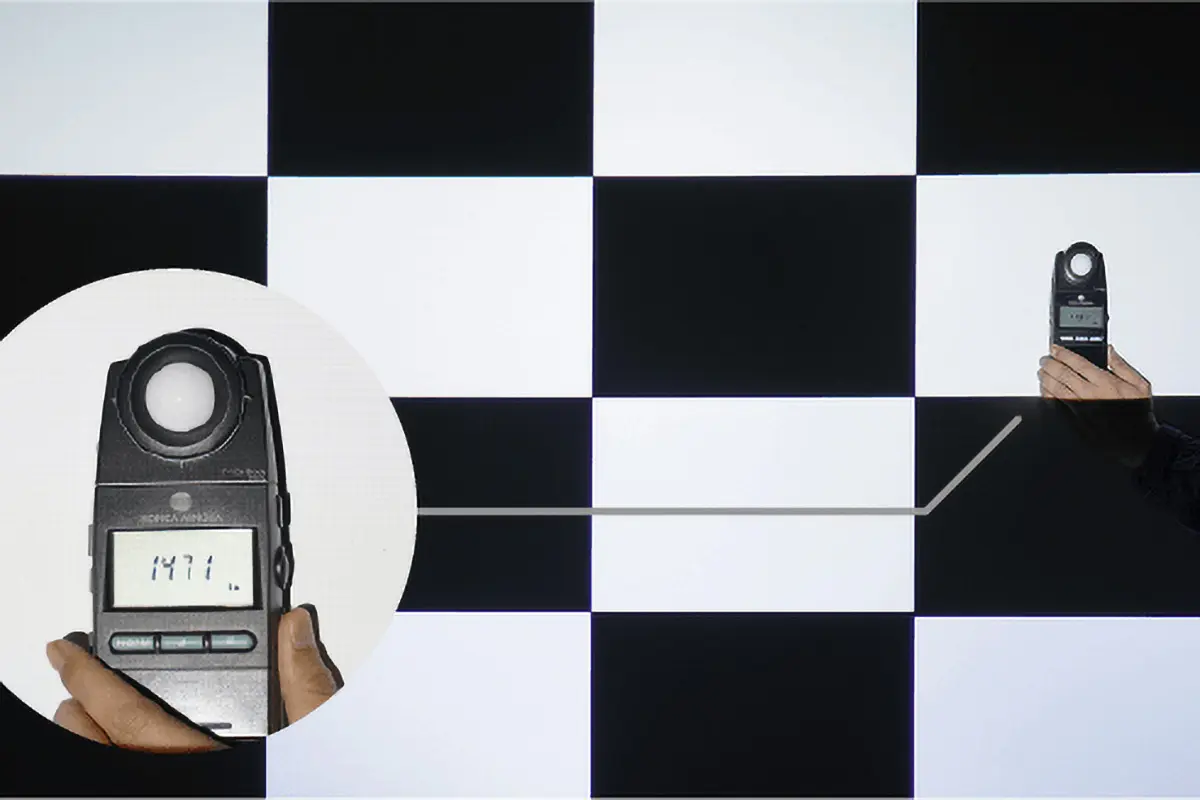

Method 2: Using Test Patterns
Another method is using special test patterns that display gradients from black to white and different gray-scale blocks to check the monitor’s contrast performance. By observing the darkest and brightest parts of these patterns, you can roughly estimate the monitor’s contrast ratio.
Method 3: Using Video Test Content
Playing video content with high contrast scenes (such as alternating deep blacks and bright scenes) can help observe the display’s performance in real-world use.
While the last two methods may not provide as precise results, they offer a visual experience that helps assess the monitor’s performance under different lighting conditions.
5.2 Why Test Display Contrast?
When you’re buying a monitor, you might already know its screen contrast ratio from the product specifications. So, is testing still necessary? Absolutely. Here’s why:
You may encounter a situation where, even though the seller lists a 4K display with a contrast ratio of “5000:1,” the actual test results show something different:
- Dynamic Contrast Ratio: 500,000:1. This is often an inflated number achieved by adjusting screen brightness or using special scenarios (like switching between full black and full white).
- ANSI Contrast Ratio: 1800:1. This is the actual contrast ratio that reflects typical display performance under normal conditions.
- Effective Contrast Ratio under Ambient Light: Only 600:1. This means that while the display might perform well in ideal conditions, its real-world performance might not meet expectations, especially in environments with ambient light.
Testing ensures that you’re getting the actual performance that aligns with your needs and the display’s real-world use.
6. FAQs
7. Conclusion
After reading this article, you should have a deeper understanding of screen contrast ratio. I hope this has helped you in choosing the right display for your needs. If you have any further questions or require more professional technical guidance, feel free to reach out to us. Our excellent technicians are always ready to assist you!